|
The need for Model Risk Management (MRM) Organisations are making major investments today to harness their massive and rapidly growing quantities of information. They are putting existing data to work and building better models with greater predictive power by applying advanced tools and techniques like Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Models are now critical, if not central, to business. Particularly in financial services which finds itself under ever increasing scrutiny. Model Governance therefore is key to maintaining control in an ever evolving regulatory landscape. However, it’s clear that for organisations to get maximum value from this type of investment they need to rethink and fine-tune their strategies. In many instances, this will also mean changing their culture and processes to deliver the control and governance needed by both Regulation and good business management. To help accomplish these goals, there needs to be a combination of advanced analytics along with a deep understanding of how to apply the correct Model Risk Management (MRM) framework that suits the business and the industry sector it’s in. Where can we use Model Risk Management? There are many processes across an organisation that fit the definition of a Model. A widely accepted identification of a model is: ’Any process which consists of Input, Calculation Throughput and an Output that drives key decision making process for the business.’ Here are some specific areas where advanced analytics and MRM are commonly used:
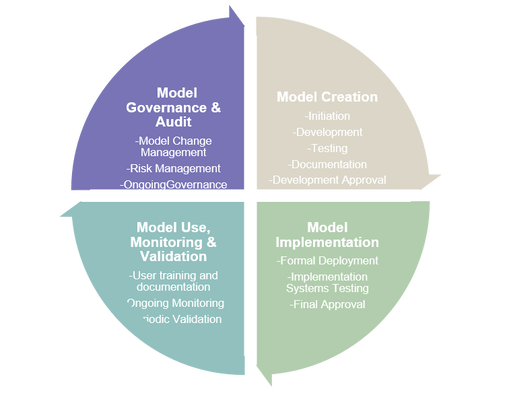
Analytics can be used at each stage of a model’s lifecycle as outlined below. Advanced Analytics and Model Risk Management Models have long been part of the toolkit used by the financial community to assess, price, and manage the various risks they face. Yet, they are also an emerging risk factor in themselves as model failure, or misuse, can seriously damage the finances, reputations, and even the solvency of firms. In addition to individual model failure, many models use the output of other models as input (e.g., a portfolio model could use modelled probability of default as input). As a result, small errors in one model might be compounded or amplified when their erroneous results are fed into other models. To mitigate this model risk, an organisation must develop and implement a suitable MRM and Model Governance framework. These governance control mechanisms are separated and outlined below to show each stage of the model lifecycle:
Figure 1 – Key Model Lifecycle Stages Model Testing and Validation – a critical area for Advanced Analytics Testing and validation are critical parts for both the development and ultimate acceptance of a model by both the business lines using the model and the external regulators that will have to review the models. Model testing and validation teams should be independent from model development teams. Three Lines of Defence Typically the Three Line of Defence (3LOD) technique is used to structure the teams, with Model Developers usually being 1LOD and Model Testers & Validations being 2LOD. Key stakeholders and model sponsors occupy the 3LOD slot. Using advanced analytics skills, model testers and validators should be in a position to challenge model developers on a regular basis. In particular, the analysis should look at all aspects of a model including inputs, analytics, reporting, and performance. Where and when needed, they should have the power to be able to prevent a model that doesn’t pass their criteria from being utilised by the institution. Testing and validation should focus on three key areas:
As already identified, sophisticated models are critically important to the success of financial institutions and fair treatment of their customers. But improperly managed and monitored, they can be dangerous to any business. Accurate control of the process and ongoing governance is key to ensuring regulatory compliance and continued business success. In my next article, I will outline the correct overview of the essential building blocks for an effective MRM framework including the importance of having a standardised model tiering procedure. If you wish to discuss any of the points raised or are interested in finding out how we can help you review or implement your own MRM and Model Governance framework, please contact us here to book your free Discovery consultation. Sources: McKinsey - advanced analytics and how it helps business functions Moody’s – the need for MRM PWC - MRM Brendan JayagopalFounder and Managing Director. Blue Label Consulting
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
brendan jayagopalBrendan launched Blue Label Consulting in 2011. With innovative use of Data through emerging data sciences such as AI and other quantitative methods, he delivers robust analytics and actionable insights to solve business problems. Archives
February 2021
Categories
All
|
Our Services |
Our Clients |
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
